Appendices
Appendix A: Ineligible list of facilities for O. Reg. 1/17
The following cannot register their activities in the Air Emissions EASR:
- A facility that is identified with a primary NAICS code that begins with a NAICS code in the following list. This means that if a 3 digit code is listed below, then any subsequent 4, 5 or 6 digit NAICS code also cannot register. For more information on NAICS codes, visit Statistics Canada website.
- 2122 (Metal ore mining).
- 2123 (Non-metallic mineral mining and quarrying).
- 22132 (Sewage treatment facilities).
- 31122 (Starch and vegetable fat and oil manufacturing).
- 31161 (Animal slaughtering and processing).
- 321111 (Sawmills (except shingle and shake mills)).
- 3221 (Pulp, paper and paperboard mills).
- 32411 (Petroleum refineries).
- 32412 (Asphalt paving, roofing and saturated materials manufacturing).
- 32419 (Other petroleum and coal product manufacturing).
- 325 (Chemical manufacturing).
- 32615 (Urethane and other foam product (except polystyrene) manufacturing).
- 3262 (Rubber product manufacturing).
- 32731 (Cement manufacturing).
- 32732 (Ready-mix concrete manufacturing).
- 32741 (Lime manufacturing).
- 3279 (Other non-metallic mineral product manufacturing).
- 331 (Primary metal manufacturing).
- 3321 (Forging and stamping).
- 33281 (Coating, engraving, cold and heat treating and allied activities).
- 332999 (All other miscellaneous fabricated metal product manufacturing).
- 336 (Transportation equipment manufacturing).
- 56211 (Waste collection).
- 5622 (Waste treatment and disposal).
- 5629 (Remediation and other waste management services).
- 81222 (Cemeteries and crematoria).
- A facility that is primarily identified by the NAICS code that begins with 3212 (Veneer, plywood and engineered wood product manufacturing). However facilities identified by the NAICS code 321211 (Hardwood veneer and plywood mills) are eligible to register with the Air Emissions EASR.
- A facility at which at least one of the following takes place:
- The land disposal of waste.
- The processing or disposing of waste by way of thermal treatment, other than the thermal treatment of the fuel described for a small wood-fired combustor that was installed at the facility on or after January 31, 2017.
- The use of a wood-fired combustor other than a small wood-fired combustor that was installed at the facility on or after January 31, 2017 and that exclusively uses wood briquettes, wood chips, or wood pellets as its fuel source. Chapter 5 of the EASR publication describes the specifications of these fuels. For the purposes of this Regulation, wood chips, wood briquettes and wood pellets that are burned in a small wood fired combustor are not considered a waste.
- The use of a plating process that uses cadmium, cyanide, chromium or nickel, including chrome plating, electroplating or electroless plating.
- The use of an electrolytic stripping process that removes cadmium, chromium or nickel from an object.
- The processing of metals outdoors, including torching, shearing, shredding or plasma cutting, other than for the purpose of routine maintenance carried out at the facility on any plant, structure, equipment, apparatus or thing.
- The operation of an alternative low-carbon fuel site as defined in O. Reg. 79/15 (Alternative Low-Carbon Fuel) which means a facility,
- That is designed to combust coal or coke for the primary purpose of manufacturing clinker, lime, iron, steel or metallurgical coke, and
- At which alternative low-carbon fuel is combusted in the place of coal or coke.
- A facility that operates an End of Life Vehicle waste disposal site and falls within O. Reg. 85/16 (EASR for End of Life Vehicle waste disposal site).
- A facility that operates a fossil-fuel electric power generator with a maximum electrical power output capacity equal or greater than 25 megawatts.
- A facility that operates a combustion source that uses biogas, biomass, coal, or waste fuel as a fuel or that uses a fuel derived from biogas, biomass, coal, petroleum coke or waste. However, this does not include the operation of a small wood-fired combustor that was installed at the facility on or after January 31, 2017 and that exclusively uses one or more of the fuels listed above for a small wood-fired combustor.
- The use of a combustion turbine.
- A facility that has a landfilling site that is no longer permitted to accept waste.
- A facility that has or previously had a site-specific air standard for a contaminant discharged from the facility.
- A facility that has or previously had a person at the facility registered in the ministry’s Technical Standards Registry for a contaminant discharged from the facility.
- Equipment that is intended to be moved from one site to another to perform the same function at each site, such as the use of mobile rock crushing equipment or mobile PCB destruction equipment.
- An activity engaged in at a facility that is located on a property that is one of a group of properties. This is defined as a single property under subsection 4 (2) of O. Reg. 419/05.
- A facility that has an activity that is exempt from having to obtain an ECA for air and noise under subsection 9 (1) of the EPA and do not require to be registered on with the Air Emissions EASR.
- Activities that are operated under a REA are not required to register with the Air Emissions EASR as long as the approval covers all activities with air and noise emissions.
Appendix B: Definitions used in O. Reg. 1/17
The following definitions are from O. Reg. 1/17 and have been included here for reference purposes.
“ACB list” means the document entitled “Air Contaminants Benchmarks (ACB) List: Standards, guidelines and screening levels for assessing point of impingement concentrations of air contaminants”, as amended from time to time and published by the Ministry and available on a Government website;
“acoustic assessment” means a detailed assessment of sound discharged into the air from sources of sound at a facility that assesses the predictable worst case sound levels at affected points of noise reception using calculations or measurements capable of accurately determining sound levels at points of noise reception;
“biogas” has the same meaning as in Ontario Regulation 160/99 (Definitions and Exemptions) made under the Electricity Act, 1998;
“biomass” has the same meaning as in Ontario Regulation 160/99;
“boiler” means a piece of equipment that includes a combustion source and that is used for the purpose of generating hot water or steam;
“combustion source” means a device in which combustible material is oxidized, resulting in the release of heat and products of combustion;
“combustion turbine” means a combustion source containing an engine that operates according to the Brayton thermodynamic cycle, in which fuel is burned and the products of combustion are allowed to expand through the blades of a rotating turbine at a high temperature;
“EASR ESDM report” means an Environmental Activity and Sector Registry Emission Summary and Dispersion Modelling report;
“EASR publication” means the document entitled “Environmental Activity and Sector Registry - Limits and Other Requirements”, setting out matters such as limits, intensity rates and requirements relating to the equipment and technology used at facilities, the operation of facilities, record-keeping and the monitoring and reporting of information relating to facilities, as amended from time to time and published by the Ministry and available on a Government website;
“EASR regulation” means a regulation made under the Act by which one or more activities are prescribed for the purposes of subsection 20.21 (1) of the Act;
“electricity generation engine” means a combustion source that is a reciprocating engine and that is used to generate electricity;
“facility” means all plants, structures, equipment, apparatuses, mechanisms or things, including surfaces and storage piles, that function as a single integrated operation and that are,
- owned or operated by the same person, and
- located on the same site;
“flue gas” means a gas that is generated by a combustion process;
“heater” means a piece of equipment that includes a combustion source and that is used to transfer heat directly or indirectly to material that is being processed;
“in-stack testing” means the measurement of the amount of combustion contaminants in the flue gas of a piece of combustion equipment.
“land disposal”, with respect to waste, has the same meaning as in Regulation 347 (General —Waste Management) made under the Act;
“licensed engineering practitioner” means a person who holds a licence, limited licence or temporary licence under the Professional Engineers Act;
“modification”, in respect of a facility, means any of the following that may discharge or alter the rate or manner of discharge of a contaminant into the air:
- the construction, alteration, extension or replacement of any plant, structure, equipment, apparatus, mechanism or thing,
- the alteration of a process or rate of production;
“NAICS” means the North American Industry Classification System maintained for Canada by Statistics Canada, as amended from time to time;
“Niagara Escarpment Planning Area” has the same meaning as in the Niagara Escarpment Planning and Development Act.
“point of noise reception” means a point described in Chapter 3 of the EASR publication at which sound discharged into the air from a source of sound at a facility is received;
“point of odour reception” means a point described in Chapter 4 of the EASR publication at which odour discharged into the air from a source of odour at a facility is received;
“Primary Noise Screening Method” means the method, published by the Ministry as updated from time to time and available on a Government of Ontario website, for determining the minimum separation distance that would result in sound levels less than or equal to the sound level limits set out in Chapter 3 of the EASR publication;
“Registry” means the Environmental Activity and Sector Registry established under Part II.2 of the Act;
“Secondary Noise Screening Method” means the method, published by the Ministry as updated from time to time and available on a Government of Ontario website, for determining the combined sound level at an affected point of noise reception;
“shut-down” means an operating condition during which the operation of a piece of combustion equipment is decreased from normal operating conditions to an inoperative state;
“site”, with respect to a facility, means the property on which the facility is located;
“small wood-fired combustor” means a wood-fired combustor that has a nominal load heat input capacity of less than three megawatts;
“standby power system” means any apparatus, mechanism, equipment or other thing, and any related exhaust stacks, fuel tanks and piping, that includes one or more electricity generation engines and that is intended to be used only for the provision of electrical power during power outages or involuntary power reductions.
“start-up” means an operating condition during which the operation of a piece of combustion equipment is increased from an inoperative state to normal operating conditions.
“thermal treatment” has the same meaning as in Regulation 347;
“wood-fired combustor” means a combustion source designed to burn wood fuel such as hogged wood fuel, wood chips, wood pellets, bark, sawdust, woodwaste, cellulosic plant material, paper or paper sludge.
Appendix C: Legislation and regulations
Environmental Protection Act, R.S.O. 1990, c. E.19
- Ontario Regulation 245/11: Registrations Under Part II.2 of the Act - General
- Ontario Regulation 1/17: (Registrations under II.2 of the Act – Activities Requiring Assessment of Air Emissions)
- Ontario Regulation 419/05: Air Pollution - Local Air Quality
Appendix D: Site/Facility example
The Air Emissions EASR regulation defines facility and site for the purposes of the Regulation. Facility means all plants, structures, equipment, apparatuses, mechanisms or things, including surfaces and storage piles, that function as a single integrated operation and that are, owned or operated by the same person, and located on the same site. Where site means the property on which the facility is located.
A property can have one or more adjacent addresses. When registering, all addresses must be identified. In Figure 3, Company 1 enters in 135 Main Street and Company 2 enters 133 and 131 Main Street as site information when registering on the EASR.
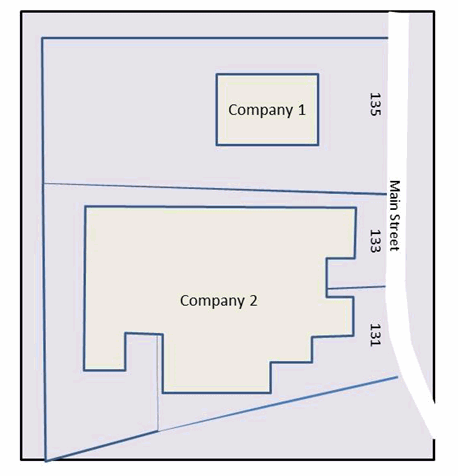
Figure 3: A depiction showing how to determine the site address if the property has one or more adjacent addresses.