Paediatric death review: analysis
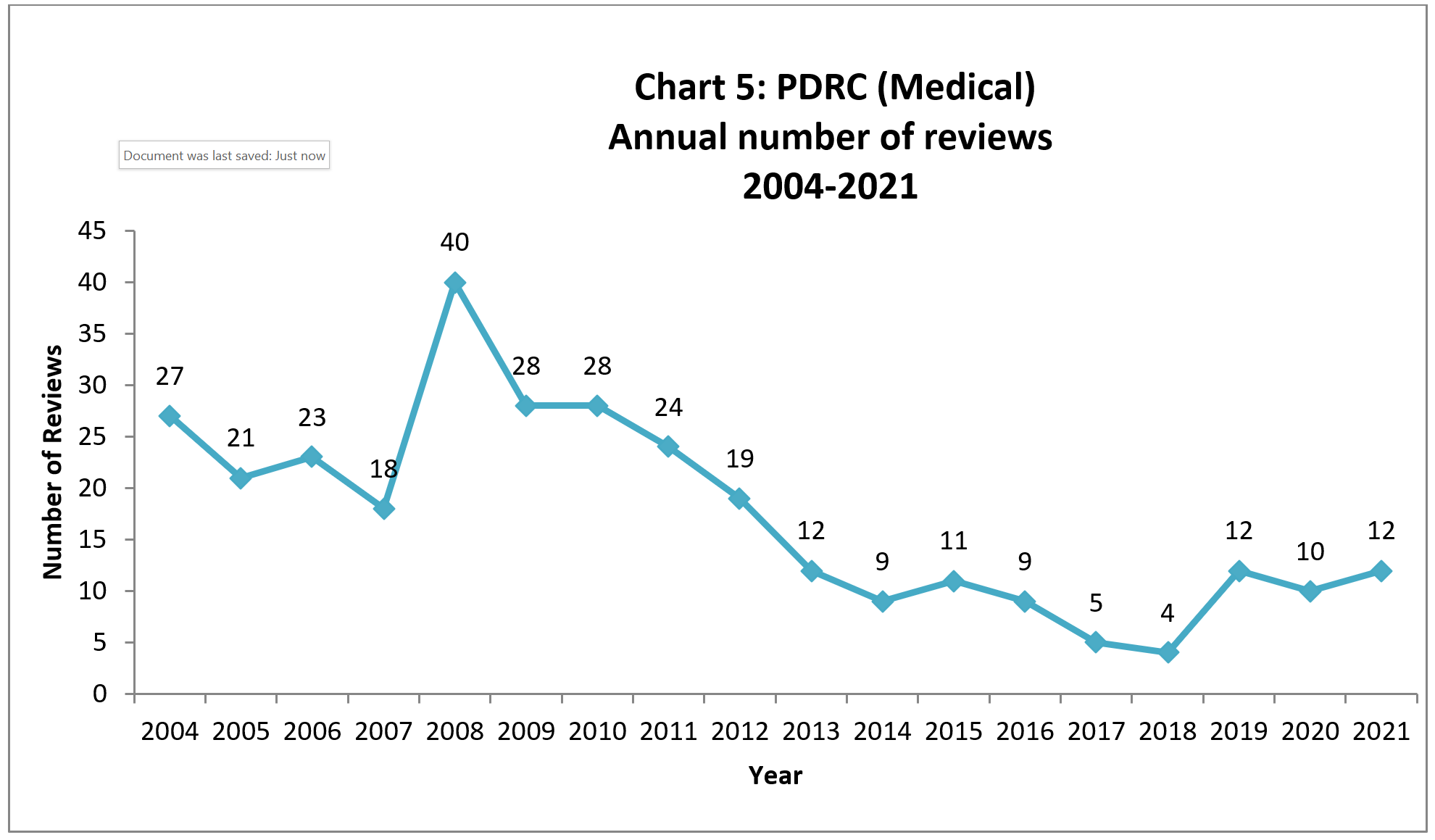
The number of PDRC-Medical reviews varies from year to year. Chart 5 illustrates the number of PDRC-Medical review from 2004 to 2021. In 2019, 2020 and 2021, 12, 10 and 12 reviews were conducted respectively.
Recommendations
One of the goals of PDRC-Medical review is informing medical systems through recommendations using a “no blame” approach. The focus is on preventing further deaths via:
- systemic changes;
- changes in professional practice
- response to emerging trends
In 2019, 9 of 12 reviews resulted in 13 recommendations. There were 3 reviews that resulted in no recommendations.
In 2020, 9 of 10 reviews resulted in 15 recommendations. One death review that resulted in no recommendations.
In 2021, 11 of 12 reviews resulted in 24 recommendations. One review that resulted in no recommendations.
Summary of recommendations made by PDRC–Medical
The recommendations made from the PDRC–Medical reviews in 2019—2021 focused on the following themes and were directed to the identified organizations:
| Organization(s) asked to respond to recommendation | Theme of recommendation(s) | Number of reviews where theme was identified 2019—2021 |
|---|---|---|
| Treating Healthcare Professional Healthcare Organization Critical Care Services Ontario OCC Regional Office Provincial Council for Maternal and Child Health Professional Association Healthcare Professional Regulatory Body | Quality of Care | 19 |
| Healthcare Organization Police Agency Local Child Welfare Agency Professional Association Healthcare Regulatory Body Death Investigation System Provincial Council for Maternal and Child Health Healthcare Association Critical Care Services Ontario Health Canada | Policy and Procedure | 8 |
| Healthcare Organization Police Agency Local Child Welfare Agency OCC Regional Office Provincial Council for Maternal and Child Health Critical Care Services Ontario Healthcare Professional Regulatory Body | Communication/ Documentation | 9 |
| OCC Regional Office Healthcare Organization | Testing | 9 |
| Provincial Council for Maternal and Child Health Treating Health Care Professionals | Transport | 4 |
| Healthcare Organization Critical Care Services Ontario Provincial Council for Maternal and Child Health Professional Associations Healthcare Professional Regulatory Body Health Canada Parachute Canada | Education/ Training | 11 |
| Provincial Council for Maternal and Child Health OCC Regional Office | Other | 3 |
Themes arising during medical reviews
Themes are often identified in individual death reviews and sometimes patterns may emerge when similar issues are observed in other reviews. Over time, the PDRC–Medical has identified and compiled themes that have been common in child and youth death reviews. The benefit of having a thematic approach is that the recurring themes can become an agent for systemic change. Over the past several years, several initiatives stemming from PDRC–Medical recommendations have enhanced paediatric health care in Ontario.
Themes by year or between 2019–2021
The cases reviewed by the PDRC–Medical in 2019—2021 were associated with six key themes. Some cases had more than one theme identified.
While these themes are consistent with past findings, by taking the extra step of evaluating for emerging trends, a refined focus for recommendations is taken with a view of systemic improvement instead of only considering the individual cases. The consistent themes, and issues associated with each, are:
Quality of care
The following treatment and/or quality of care issues were identified:
- Triaging consultations
- Resuscitation team dynamics
- Recognition and treatment of paediatric shock
- Standards and certification of ER staff/referral to Criticall
- Early recognition of paediatric surgical conditions necessitating urgent or emergent transfer to a referral centre
- Importance of the timely measurement of a blood glucose level in an acutely ill and/or neurologically depressed child
- Equipment preparedness protocols
- Paediatric airway management
- Recognition and management of acute abdomen in children
- Identifying findings compatible with congenital diaphragmatic hernia
- Clinical and radiologic indications for sustained in-hospital monitoring or hospital admission in infants and children with acute respiratory illnesses
- Resuscitation guidelines for infants, including choice of medications
Policy and procedures
- Collaboration in complex child protection cases to ensure that suspicious injuries or other concerns for maltreatment are appropriately assessed
- Acceptance of unstable surgical cases and operative and perioperative management of an unstable paediatric patient
- Cardiac assessment prior to discharging patients with complex single ventricle physiology
- Identification of related cases referred to the OCC
- Triage protocols and procedures to support rapid diagnosis and removal of button batteries, as well as follow up investigations to assess the degree of on-going injury
- Car seat standards, specifically modifications to meet the positional and transportation needs of preterm and low birthweight infants
- Engagement of Paediatric Critical Care Response Team (PCCRT) Program in life and limb situations, and early activation of Criticall
Communication and documentation
- Importance of physician orders being clearly written and accurately transcribed
- Communication and consultation with subspecialty care teams in the management of medically complex cases
- Publication of the hazards associated with button battery ingestion
Testing
- Recommendations for further cardiac evaluation and/or genetic testing of family members
- Use of ultrasound assessment of the urinary tract in patients with renal impairment to seek reversible causes
- Availability of capillary blood sampling and point of care testing
Transport
- Transport and transfer protocols and procedures of critically ill children and youth
- Adding additional trained personnel to assist with resuscitation over long transports
Education and training
- Education on safe sleeping environments and practices to all clients and caregivers
- Education on the dangers of battery ingestion in children and highlighting the potentially fatal consequences
- Maintenance of certification in paediatric advanced life support (PALS)
Other
- Recommended change(s) to cause and manner based on additional testing.
- Potential funding opportunities to assist families with ongoing medical costs that may exceed their individual financial resources