This page was published under a previous government and is available for archival and research purposes.
Innovation
The history of electricity in Ontario is one of constant innovation and this is still true today. Ontario maintains its place as an innovation leader because of accomplishments with the Smart Grid. The installation of sensors and computer chips into formerly passive distribution networks not only allows many utilities to detect and fix outages quickly, but will also enable Ontarians to better manage their personal energy use.
Demand for services and apps, to enable consumers to better manage, monitor and control their energy use is increasing. According to a recent study by Accenture Consulting, Actionable Insights for the New Energy Consumer, an increasing number of consumers … "are seeking added value, personal connection and products and services that align with their lifestyles – all of which go beyond the traditional energy experience."
Ecobee delivers intelligent energy management solutions for commercial properties. The company works with local utilities in the deployment of its Programmable Communicating Thermostats, which provide automated energy conservation through demand response programs.
Enbala’s smart grid technology platform is helping Ontario to maintain grid reliability. By connecting a network of large-scale commercial and industrial electricity users to their versatile GOFlexTM platform, they can automatically increase or decrease electricity consumption in response to moment by moment changes in the electricity needs of the grid. This will help Ontario integrate its renewable energy sources more efficiently and reliably.
Team Ontario is a collaboration of more than 100 students from Carleton University, Algonquin College and Queen’s University selected to compete in the US Department of Energy Solar Decathlon. Team Ontario designed and built ECHO (ECological HOme), a "smart" home that incorporates modern technologies such as predictive shading, real-time energy monitoring, an integrated mechanical system and a user-friendly mobile application to control features of the home.
Energate is developing tools that make it easier for consumers to monitor and manage their home energy use and costs. Energate’s software, mobile applications and devices such as smart thermostats and in-home energy displays also help to manage the system by reducing peak demand. The Smart Grid Fund is helping Energate test and demonstrate these tools for consumers in homes across Ontario, including Peterborough, Vaughan, and Cambridge.
Ontario has undertaken a number of initiatives to help utilities take on innovation challenges. These initiatives are building a thriving smart grid ecosystem that can lead to innovation that both enhances the grid’s operation and improves asset management to help mitigate system and customer costs.
The Smart Grid Fund
The $50-million Smart Grid Fund was launched in 2011 to help local distribution and Smart Grid companies test and build the technologies needed to modernize the grid. The fund currently supports 11 organizations that are developing applications that track energy use, balance voltage on the grid, and automate control systems for LDCs. These smart grid solutions will also help LDCs integrate new promising technologies into Ontario’s electricity system that could help operators use grid assets more efficiently, including storage and electric vehicles.
Technological innovation from the Smart Grid could also help bring clean energy to remote communities that have economic challenges connecting to the province’s transmission grid. These communities, which currently rely on diesel fuel to generate electricity, could have their own micro distribution grid. This would integrate and balance diesel generation with the electricity that comes from wind, solar, storage and hydroelectric resources.
The Smart Grid Fund helps Ontario businesses compete with advanced technology companies from around the world. It has already led to the creation of more than 600 jobs. According to the Ontario Centres of Excellence, our growing cluster of energy technology entrepreneurs is developing the products that will drive the jobs of tomorrow. Supporting this emerging industry is in Ontario’s best interests.
Solantro Pilot Program
The pilot demonstration project will field test technologies for grid-ready (plug-and-play) AC photovoltaic that improve economics, reliability and performance of solar energy. The pilot will focus on Nano and Micro-inverters and DC Optimizer Reference Designs. The project will be conducted between 2012 and 2015.
Inverters play a crucial role in the performance of a solar panel: they convert the direct current from solar panels to alternating current that then can be used directly, stored or fed into the power grid. Reference Designs allow developers to fine tune the DC Optimizer to maximize the energy produced by the solar panel.
The result is a plug-and-play integrated circuit chip (the inverter) on the back of each solar panel that constantly optimizes efficiency and reduces the costs of design and installation.
Energy Data and Green Button
The government believes that smart meter data can be used in ways that go beyond supporting customer billing. While respecting the principles of privacy and security, new value-added services and applications for consumers could be developed by enabling better access and analysis of electricity consumption data. This type of data is essential to designing efficient and effective programs to further benefit consumers.
An important example of providing consumers with access to data is the Green Button Initiative. The Green Button Initiative provides customers with access to their electricity consumption information in a standardized format. Developers will be able to use the data to provide innovative software applications that allow consumers to view and manage their energy use. In October 2013, Ontario announced the Energy Apps for Ontario Challenge, offering $50,000 to support the best new apps that use the Green Button standard.
Ontario has made significant progress with its Green Button Initiative since it was launched in 2012. Seven LDCs have implemented the first phase of the program, providing access to Green Button to almost 60% of the province’s electricity customers. More LDCs have signaled their intention to follow quickly.
The next phase of the initiative, Connect My Data, will allow customers to automate the transfer of data securely to mobile and web applications that can be used on computers, smartphones and tablets. London Hydro and Hydro One launched the first Connect My Data pilots in November 2013, giving their customers innovative and creative applications that will help them manage and conserve their electricity use.
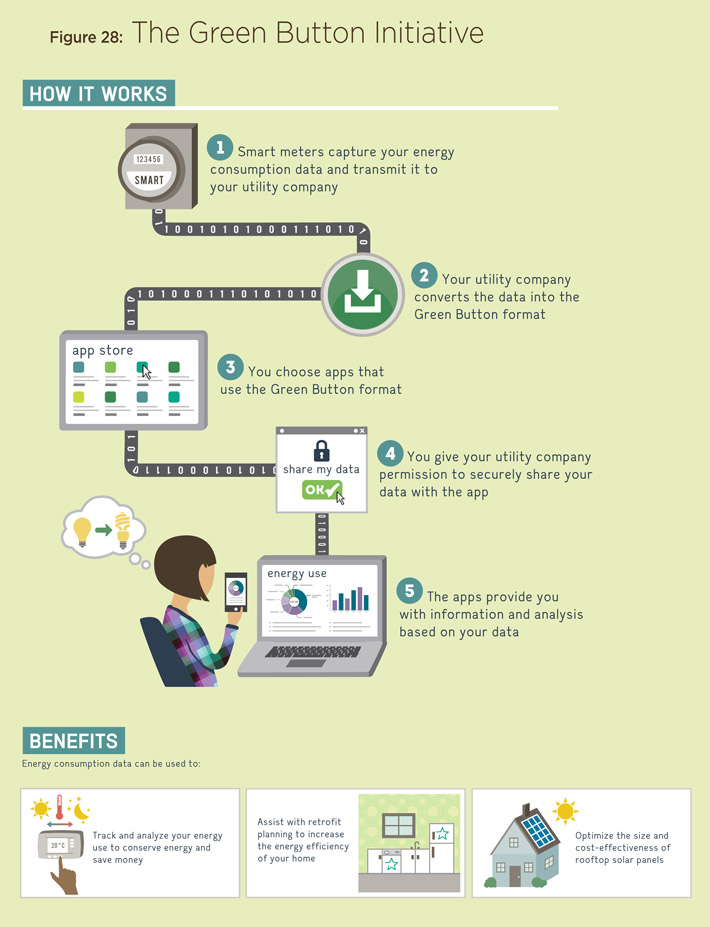
A flowchart with graphics and text. How it works:
- Smart meters capture your energy consumption data and transmit it to your utility company.
- Your utility company converts the data into the Green Button format.
- You choose apps that use the Green Button format.
- You give your utility company permission to securely share your data with the app.
- The apps provide you with information and analysis based on your data.
Benefits: Energy consumption data can be used to: Track and analyze your energy use to conserve energy and save money. Assist with retrofit planning to increase the energy efficiency of your home. Optimize the size and cost-effectiveness of rooftop solar panels.
Energy Storage
Energy storage technologies have the potential to revolutionize the electricity system, increasing its efficiency, lowering costs and increasing reliability for the consumer. With storage, electricity could be stockpiled during periods of low cost generation, and then used when demand and prices are highest.
Storage technology offers the potential to increase the useable energy from renewable energy sources.
The IESO has been integrating new technologies to correct small, sudden changes in the electric current frequency to ensure the stability of our electricity system. Ontario is home to a number of innovative companies that are at the forefront of the energy storage sector.
By the end of 2014, the government will include storage technologies in our procurement process starting with 50 MW and assessing additional engagement on an ongoing basis.
This will include:
- Commissioning an independent study to establish the value of energy storage’s many applications throughout the system;
- Examining the opportunities for net metering and conservation policies to support energy storage; and
- Providing opportunities for storage to be included in large renewable procurements.
The government also intends to initiate work, on a priority basis, to address regulatory barriers that may limit the ability of stored energy resources to compete in Ontario’s electricity market. For example, some energy storage applications are currently required to pay various retail, uplift and Global Adjustment charges twice - once when energy is captured and again by the end-user.
In Summary
- Ontario’s energy sector is an innovation leader. The government will seek to expand the Smart Grid Fund and build on previous success. The Smart Grid Fund has created more than 600 jobs and supported 11 projects developing innovative technologies.
- The government intends to initiate work, on a priority basis, to address regulatory barriers that limit the ability of energy storage technologies to compete in Ontario’s electricity market.
- By the end of 2014, the government will include storage technologies in our procurement process, starting with 50 MW and assessing additional engagement on an ongoing basis.
- The new competitive procurement process for renewable energy projects larger than 500 kW will also provide an opportunity to consider proposals that integrate energy storage with renewable energy generation.